
Blood Processing





| In the ABO blood group system, there are 4 main blood groups, namely, A, B, AB and O. ABO blood group is of paramount importance in blood transfusion because incompatible blood group transfusion can be fatal. |  Blood grouping autoanalzyer Blood grouping autoanalzyer |
 ABO and Rh(D) blood group testing ABO and Rh(D) blood group testing |
There are 2 types of Rh(D) blood group: positive and negative.
Therefore, together with the ABO blood groups, there are 8 major blood group combinations:
Table of 8 major ABO & D blood group combinations
| O+ | O- |
| A+ | A- |
| B+ | B- |
| AB+ | AB- |
In addition to anti-A and/or anti-B, donor blood may contain atypical antibodies to other red cell antigens, which may cause adverse reactions in blood recipients. Therefore, blood testing on donation samples shall include screening for atypical red cell antibodies.
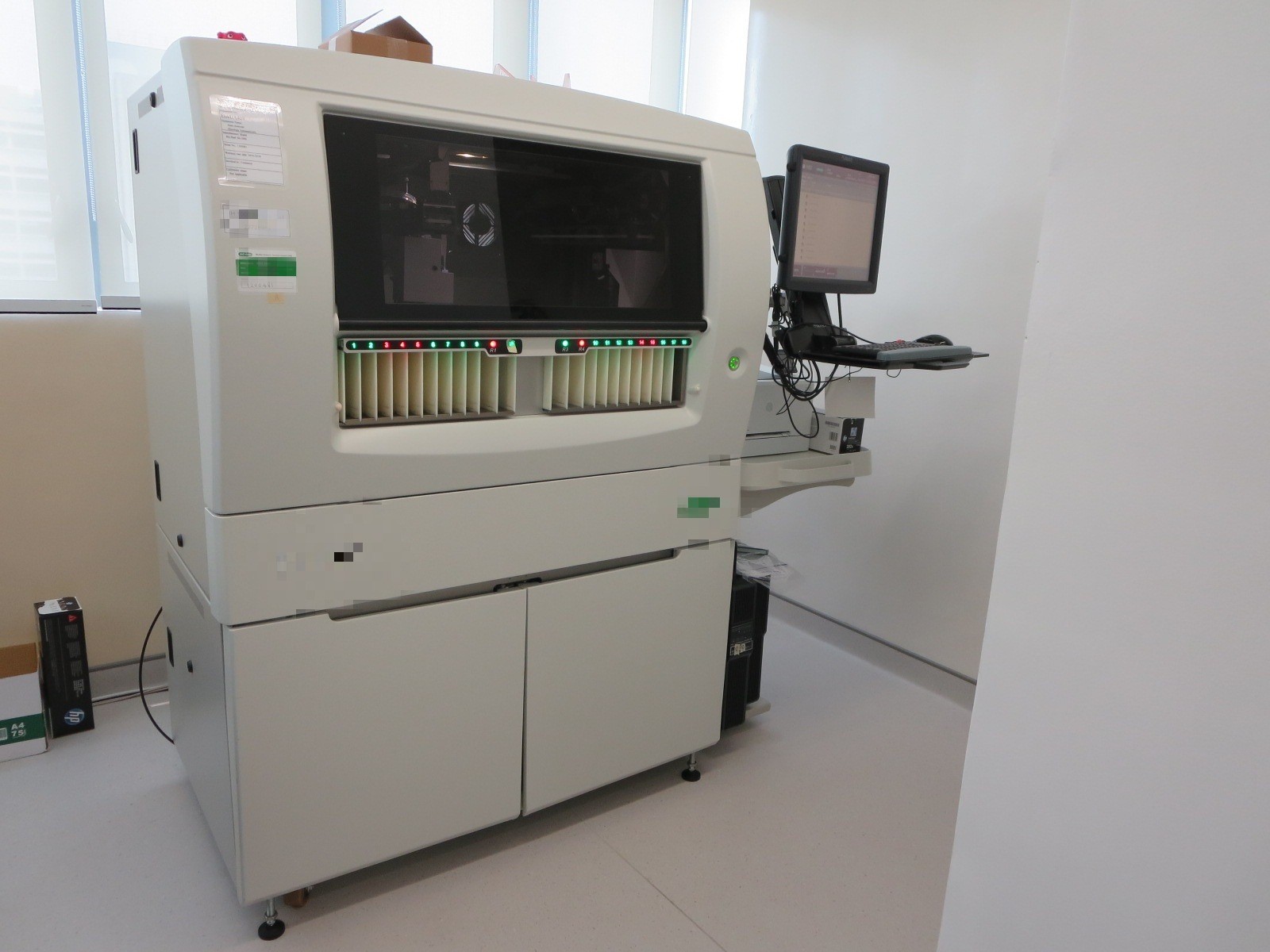

To protect patients' safety, every unit of blood will be tested by automated system to ensure they are negative for transfusion transmitted infections.
- HIV Antigen, Antibodies and RNA
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and DNA
- Hepatitis C Antibodies and RNA
- HTLV Antibodies
- Syphilis Antibodies
- Bacterial surveillance for every unit of platelet concentrates
Optional testing include:
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Antibodies
|
|
|
|
|
| Before blood components are issued to hospitals for clinical use, every unit of blood products are labelled with donation numbers for enhanced traceability, blood group, product types and eye-readable information, expiry date and other product properties. |  Labelled red cell units Labelled red cell units |
 Whole blood in quadruple bags Whole blood in quadruple bags |
 Components separation Components separation |
 Leucocyte depletion Leucocyte depletion |
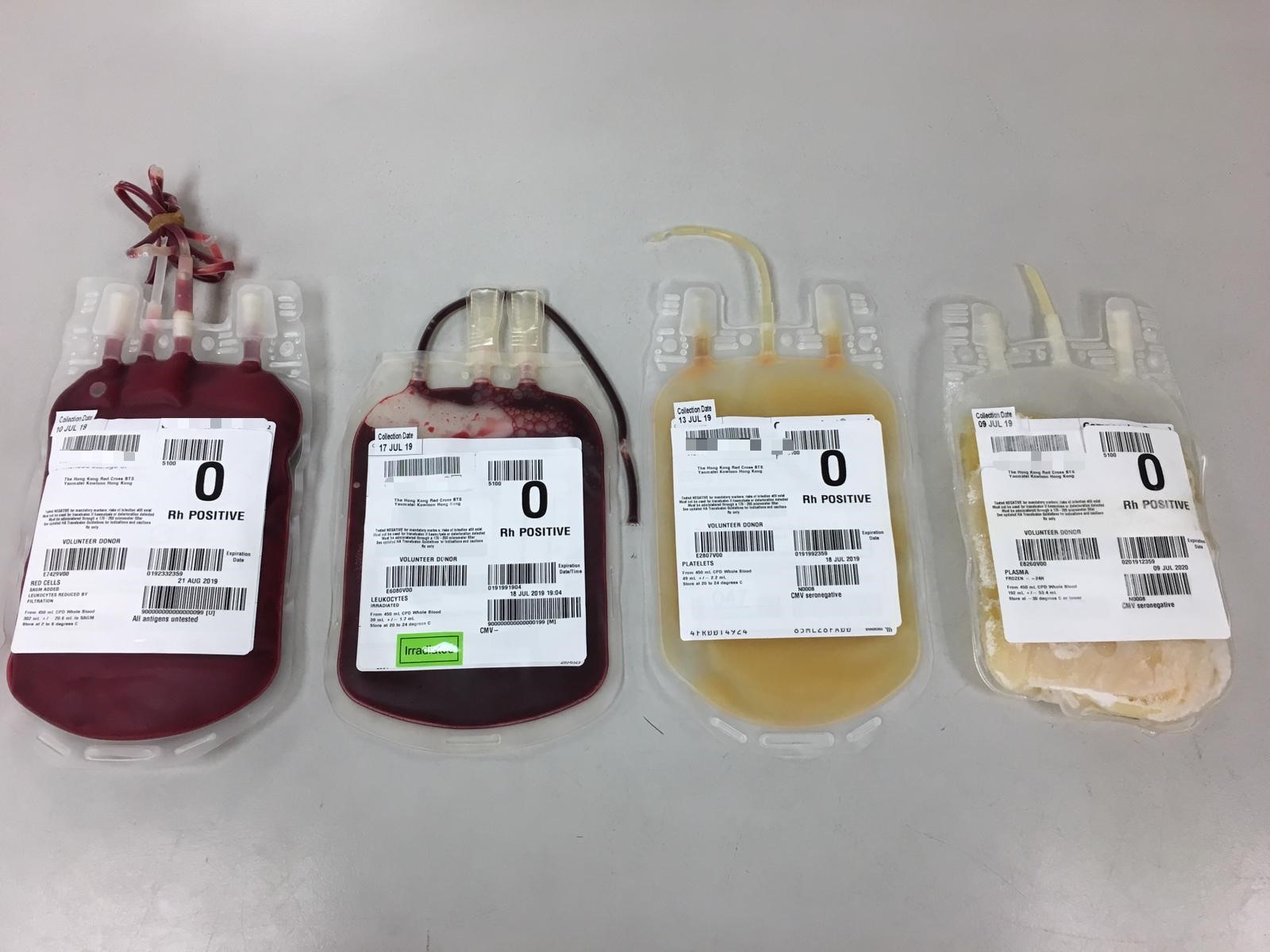
Approximately 98% blood collected in quadruple blood bags will be processed into different blood components to meet patients’ transfusion requirement:
Red Cells - used in patients with anaemia and massive bleeding; great than 90% of the distributed red cell units have been leucocyte depleted to minimize transfusion reactions.
Platelets - used in the treatment of thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) or platelet dysfunction to prevent bleeding.
Frozen Plasma - provide coagulation factors to coagulation factor deficiency patients.
Cryoprecipitate - provide fibrinogen, coagulation factor VIII and factor XIII.
Leucocytes - for treatment of patients with severe neutropenia and persistent bacterial and/or fungal infections, but not responding to antibiotic treatment.
Blood Component storage temperature and shelf life
- Whole Blood
- Storage Temperature and Condition: 2 - 6 °C
- Shelf Life: 28-35 days
- Red Cells
- Storage Temperature and Condition: 2 - 6 °C
- Shelf Life: 42 days
- Platelets
- Storage Temperature and Condition: 20 - 24 °C with continuous agitation
- Shelf Life: 5 days
- Frozen Plasma
- Storage Temperature and Condition: Below -30 °C
- Shelf Life: 365 days
- Cryoprecipitate
- Storage Temperature and Condition: Below -30 °C
- Shelf Life: 365 days
The Storage and Issue Section is responsible for the monitoring of the blood demand and supply in Hong Kong and also blood storage and utilization. It operates 24 hours a day. Every year the BTS provides about 470,000 units of blood components to all patients in Hong Kong hospitals.
Blood donor information, donation records, blood testing results and blood processing information are stored in the blood bank computer system. Before blood components are issued to hospitals, the computer system will automatically check for the component status to ensure only safe blood will be issued for transfusion use. The computer system has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) and is under strict control.

 Automated analyzer for testing of:
Automated analyzer for testing of: Automated analyzer for testing of:
Automated analyzer for testing of: Automated analyzer for testing of:
Automated analyzer for testing of: Analyzer for testing of:
Analyzer for testing of: